How To Fix A Manual Action
December 22nd, 2015 by
In recent weeks, there’s been chatter about a large influx of manual actions. This got me thinking: how many people actually know how to fix manual actions? Stay tuned, ’cause you’re gonna learn today!
But First, the Basics: What Is a Manual Action?
A manual action is a manual penalty applied to a website by a member of Google’s Web Spam team. According to Google, there are a few common types of manual actions:
- Hacked site
- User-generated spam
- Spammy freehosts
- Spammy structured markup
- Unnatural links to your site
- Thin content with little or no added value
- Cloaking and/or sneaky redirects
- Unnatural links from your site
- Pure spam
- Hidden text and/or keyword stuffing
In today’s post, we’ll be discussing a few of the most common types of manual actions.
How Do I Know My Site Has a Manual Action?
SEO practitioners know that performance fluctuations are expected, especially since Google’s algorithm is constantly changing. If you’re beginning to see your website rankings drop consistently, that’s usually an indicator of a possible manual action (or partial manual action). However, if you’re unsure, check out Google Search Console (aka Webmaster Tools for those late to the name-change party)! Once in the Search Console, you will see one of two actions displayed on the Manual Actions page:
- Site-wide matches
- Partial matches
Each action will display a reason as to why your site received the action, as well as how the action will affect your site.
So My Site Has a Manual Action…What Now?
The good news: we can fix this! The bad news: fixing a manual action takes quite a few steps. The first thing you will want to do is determine what kind of manual action your site has. If you see this message, this means that Google has detected a pattern of unnatural deceptive or manipulative links pointing to your site. According to Google, here are the recommended actions to take:
First, review Google’s Webmaster Guidelines on linking.
Next, follow the steps below to identify and correct the violation(s):
- Download a list of links to your site from Search Console. You can download your links arranged either by hostname (Links to Your Site > Who links the most > Download more sample links) or in chronological order (Links to Your Site > Who links the most > Download latest links).
- Check this list for any links that violate our guidelines on linking. If the list is large, start by looking at the sites that link to you the most or links that were created recently (in the last few months).
- For any links that violate our guidelines, contact the webmaster of that site and ask that they either remove the links or prevent them from passing PageRank, such as by adding a rel=”nofollow” attribute.
- Use the Disavow links tool in Search Console to disavow any links you were unable to get removed.
Once you’ve removed or disavowed the unnatural links, the last step is to submit a reconsideration request. A reconsideration request is a formal request to Google to reconsider giving your site a penalty. You will want to let Google know about everything you did to clean up your site, including documentation about the links you removed or tried to remove.
Here comes the bad news: once you submit the request, you have to be patient.


I know, people. I know. Ain’t nobody got time for that! BUT it will all pay off on that beautiful day when Google sends you that wonderful message in Search Console and approves your reconsideration request!
FYI, this will be you:


Hacked Site…Uh Oh!
Google may give your site a partial manual action if it notices that your site has been hacked. If you check the manual actions tab in Google Search Console, you will see a notice called “Hacked Site.”
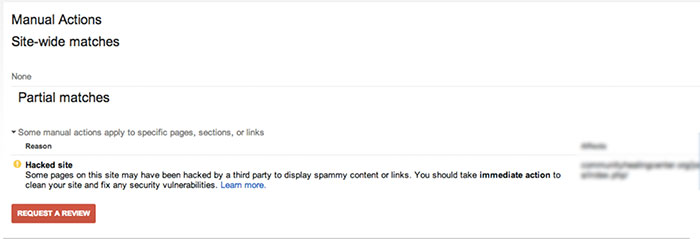

According to Google’s Web Spam team, there are a few steps you will want to take if you’re the victim of a hacking:
- Contact your host provider.
- Quarantine your site by taking your site offline (change all passwords and check new user accounts).
- Check the Google Search Console.
- Assess the damage. If your site was hacked with spam, the display warning will be “This site may be hacked.” If you’ve been hacked with malware, the display warning will state “The site may harm your computer.”
- Identify the site’s vulnerabilities and list them out.
- Clean up the website to prevent future security problems.
Once all hacked content is removed, “Request a Review” in the Google Search Console. Again, patience. Ugh.
Thin Content with Little or No Value
For the non-SEO practitioners, you might be thinking, “What does that mean?” In a nutshell, Google launched a quality update in May 2015, specifically for onsite content. This means Google is placing more of an emphasis on sites producing quality content and penalizes those with content that is not useful to visitors.
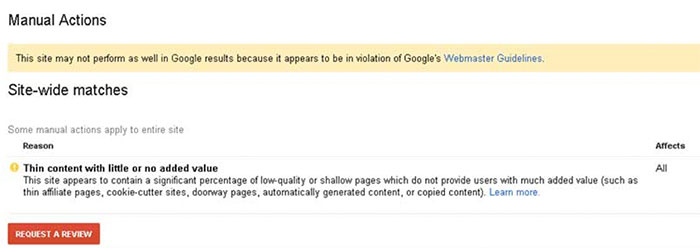

How to Fix Your Content, According to Google:
- Remove any duplicate content from your site that is found anywhere else on the Internet.
- Eliminate affiliate links on pages with little to no valued content, or add some value to the page’s content.
- Get rid of auto-generated content pages.
- Improve the website content to provide significant value for your site visitors!
Once again…cue the reconsideration request.
Remember, patience is a virtue!


Kim,
The GIF’s are too good.
I came across a post regarding the reconsideration request. It says about, while applying the reconsideration make sure you write in a good way with details. So that the google manual team will revoke the penality sooner than usual time.
Kind of persuation tricks apply here.
Hope that helsp to someone who are trying to apply for reconsideration request. To be frank, I applied that and it helped.
Cheers
Suresh