What’s Black & White & May Have Killed Your Site in 2014? This Year’s Top 3 Algo Updates
December 22nd, 2014 by
In 2014, there were numerous algorithm updates that changed the world of SEO—for the better. Google uses a finely tuned (and ever-changing) algorithm to sort search results in a way that best caters to the searcher. In order to perfect this art, Google turns out algorithm updates, both minute and massive, regularly (and sometimes not so regularly). As such, SEO is always evolving to match this quickly turning tide, which is why it’s best to focus on creating a site that will best benefit the end user.
Looking back on the past year, there were many, many, MANY updates of note. So let’s just focus on the top three major hitters.
Panda 4.0
About
Being in the top three is no small feat, and kicking off the list of top algorithm updates of 2014 is Panda 4.0. On May 19th, Panda 4.0 rolled out, affecting about 7.5% of English-language queries. Though there was another major Panda update in 2014, Panda 4.1, the effects of this second Panda update were less noticeable than those of its predecessor, “only” affecting about 3-5% of queries.
Generally, Panda updates are geared towards high-quality content. Their goals are twofold:
- To stop sites with low-quality content from working their way into Google’s top search results
- To reward high-quality content with more presence by pushing sites with thin content down in SERPs
What did it do?
Panda 4.0’s effects did not stray from the Panda expectation. Some of the observed changes that occurred to sites as a result of Panda 4.0 were that it:
- Penalized aggregated content
- Aggregated content relates to sites that compile content from other sites. A well-known site that utilizes aggreged content is Buzzfeed, though Buzzfeed seemed to fare this update well.
- Penalized thin content
- There were 2 major types of sites with thin content that were affected:
- Sites lacking quality, long-form content throughout
- Sites with strong hierarchical structures that may contain quality, long-form content on key pages but contain thin content on higher-level category pages
- There were 2 major types of sites with thin content that were affected:
- Rewarded high-quality content
- Sites with reputable, long form, user-friendly content
How it changed SEO
Quality content = good content + positive user experience. The major takeaway from Panda 4.0 is not a new one. User experience is always an important factor, but it’s one that can get lost in pursuit of developing long-form content. When developing quality content, an emphasis should also be placed on how the content is viewed.


Images
Paragraph after paragraph about your service offerings is likely a wasted effort without visual aids to break up text and give users a new means of understanding.
Internal Links
Do you have before and after images? Related blog posts? Anything to give the reader more info? Add links to give users a reason to click through more of your site.
Mobile Experience
Now have you considered mobile? Site visits from mobile users are always increasing. Are you providing mobile visitors a good viewing experience that is specific to mobile and easy to navigate and read?

Though not a part of the Panda update, Google is now providing information in SERPs stating whether a site is mobile-friendly or not. This effectively allows users to skip over results they know cannot be easily viewed on their device, and it furthers the importance of ensuring that your site provides a positive user experience for searchers on all devices.
“Pigeon”
About
A few short months after Panda 4.0, a new breed of animal entered the circus of algo updates when Google rolled out “Pigeon.” Unlike Penguin and Panda updates, Pigeon was not a penalty-based update (aimed at cleaning the SERPs from low-quality sites), but a core change to the local search ranking algorithm. Many different types of businesses were affected by Pigeon. Some of the industries that saw a big effect from Pigeon were real estate, restaurant, hotel, retail, and more.
What did it do?
Overall, Pigeon dramatically altered some local results and modified how they handle and interpret location cues. This update is supposed to be a move toward a better user experience for mobile users, with results more concentrated in number and in proximity to your location. Google has also stated that Pigeon helped develop closer ties between the local algorithm and the core algorithms.
How it changed SEO
Some of the major changes that occurred as a result of this update were:
- The disappearance of local listing packs from a large number of SERPs
- A stronger emphasis placed on relevant directories in search results, leading more SERPs to become directory-heavy rather than heavy with individual businesses’ sites.
- A switch in focus of local ranking factors
- Local rankings are expected to depend more on website authority and less on traditional local ranking signals
- A change to the way in which location cues are interpreted, with results more concentrated in number and in proximity to your current location
Penguin 3.0
About
Last, and certainly not least, this list would not be complete without mention of our long-lost “frienemy,” Penguin. This year, the story of our love/hate relationship with the Penguin algo update was mostly one of love and longing as we patiently awaited its arrival after a yearlong hiatus. Much like preparing for the arrival of Santa, webmasters spent their year diligently reviewing and cleaning up backlinks in an effort to wind up on Penguin’s “nice” list. Finally, Christmas morning came on October 17th when Penguin 3.0 began rolling out, initially affecting less than 1% of US/English queries.
What did it do?
Generally speaking, Penguin updates focus on the level of natural linking behavior. This filter primarily affects websites with a high volume of lower-quality links. For those sites who were affected by the Penguin updates of 2013 and took the initiative to clean up low-quality links in 2014, a positive effect was likely realized after Penguin 3.0.
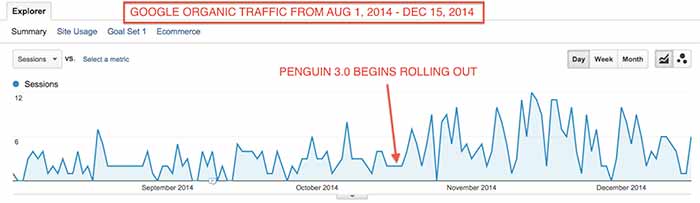

Specifically, Penguin 3.0 also began a movement to begin regular refreshes, much like Panda. As a result, many webmasters have observed major changes since Penguin 3.0, dubbing these major changes Penguin 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, and 3.4.
How it changed SEO
Penguin 3.0 resulted in 2 major industry changes in how Penguin updates are processed and anticipated:
- Google has stated that they will move toward regular refreshes of Penguin 3.0, much as they have done with Panda. In the past, Penguin updates have been processed offline and pushed live on a specific date and time. With this new change, Google is indicating that they will be making changes to the algo within their live rankings processes.
- Google broke its “no major updates during the holidays” promise on Thanksgiving Day when Penguin 3.1 occurred. Though Google considered this Thanksgiving Day fluctuation a part of their initial Penguin 3.0 rollout, rarely do updates take this long and cause major fluctuations late in the game.


Takeaways For 2015
So whether Panda, Pigeon, or Penguin affected your site in during 2014, we hope you have been able to use the plethora of circulating information to bounce back. If not, you can always contact Search Influence to help you formulate a specialized plan.
The big takeaway, however, is that algorithm updates are to be expected, so it’s best to prepare for them ahead of time by making your site as user-friendly as possible. We don’t know what’s headed for us in 2015, but rest assured, it will probably be as eventful as 2014.

